Component architecture examples
This section focuses on the main architecture design patterns recommended by Blue Prism. Whilst other configurations are possible, these should be discussed with your Blue Prism Technical Consultant to determine their scalability, security, and resilience.
Whilst the majority of Blue Prism environments are built on virtualized hardware, the components are equally suited to physical equipment. As such, the architecture diagrams in this guide do not differentiate between physical or virtualized configurations.
The latest information about the minimum specifications of each Blue Prism component can be found in Blue Prism software and hardware requirements.
In each of the following examples the specifications for the Blue Prism runtime resources and Blue Prism interactive clients remain the same.
The specification of interactive clients and the runtime resources used for development must meet the collective recommendations of all applications to be automated on that device, for example, SAP, Office, Temenos, or FiServ. A useful indicator is to base the specification on an equivalent device used by an end-user to perform the tasks that are to be automated.
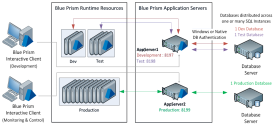
Data-center secured: 25 runtime resources
Controllers and process developers should use their own physical PC as interactive clients, rather than virtualized runtime resources. Runtime resources and application servers can optionally be configured on virtual machines.
The following diagram shows default and configured port numbers, for details of the default ports for each component, see Default ports .
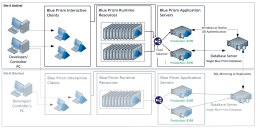
Data-center secured with disaster recovery (DR): 100 runtime resources
An environment which is entirely secured within the data center and which illustrates:
- Two sets of 50 runtime resources connected to load-balanced application servers.
- Interactive clients which are used remotely.
- A DR site with up to 100 runtime resources and a single application server connected to a replicated copy of the database.
The load balancer indicated in the diagram above can be your organization’s preferred choice.
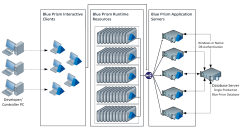
Data-center secured: 500 runtime resources
An environment which is entirely secured within the data center and which illustrates:
- Five sets of 100 runtime resources, each with a dedicated application server.
- Interactive clients which are used remotely.
Advantages and constraints of virtualized hardware
Whilst the majority of Blue Prism environments are built on virtualized hardware, the components are equally suited to physical equipment. The following table lists the advantages and constraints of the use of virtual environments.
|
Advantages |
Constraints |
|---|---|
|
|
 Docs
Docs